
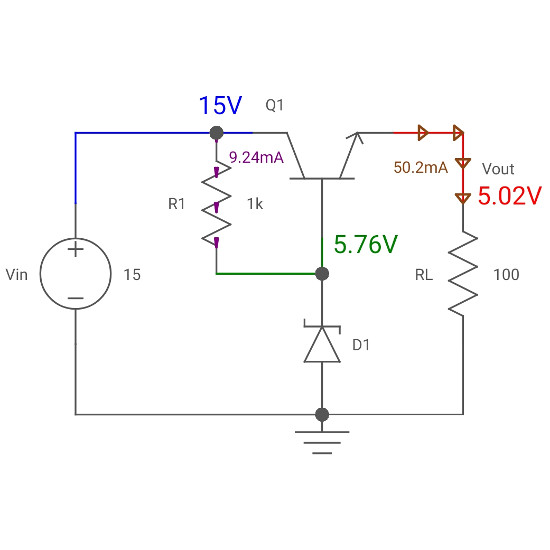
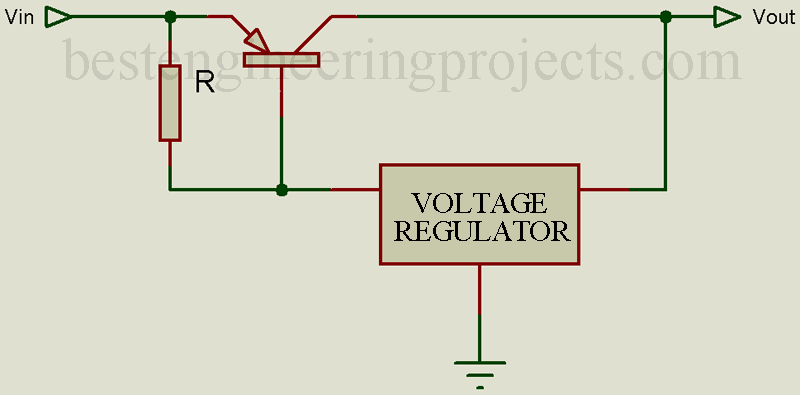
A functional diagram works as a useful model so that the principles of a series regulator model could easily be understood. In figure 2, a functional block diagram of a series type regulator has been shown. There are two types of voltage regulators.Ī regulator, the control element (normally a transistor) which is mounted within a series of input voltage and output voltage, is known as a series voltage regulator.
Thus, the objective of a regulator is to eliminate any changes in output voltage (which may result from a load change, input voltage changes, or temperature change). It compensates for every tendency of output voltages and increases or decreases supply voltage automatically according to requirement. It is also called a closed-loop control system because it provides feedback via examination of output voltages. Figure1Ī voltage regulator is a device or set of devices designed in such a manner that it maintains the output voltage of a power supply constant to the maximum possible extent. (Percent voltage regulation value of a correct power supply is zero) i.e. Its percent voltage is called regulation.
#Power transistor voltage regulator full
Measurement of efficiency of a power supply, through which it could be ascertained, how better a power supply is, enables a power supply to keep it on a constant voltage between no load and full load conditions. In figure 1, no-load and full load conditions of power supply have been illustrated. when no current is being received from the supply (zero current), terminal voltages of the power supply at that time are called no-load voltages. No-load voltages (V NL) are open circuit terminal voltages i.e. When full load current is being achieved, at that point, terminal voltages of the power supply are called full load voltages (V FL).
Specifications of a power supply also contain its full load current ratings (I FL), which is the maximum current received through the supply. However, output voltages, in a practical power supply change with the value of its load current (usually with an increase in load current, voltages of power supply decrease or drop). Series Voltage Regulator and Shunt Voltages Regulator- in this article, we will discuss series and shunt voltage regulators in detail.Īn exemplary power supply always has constant voltages on output terminals, irrespective of the values of current received (or within its rated current capacity, whatever the value of load it is connected with).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
